Difference between revisions of "Master Do-files"
Mrijanrimal (talk | contribs) |
Maria jones (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Components of a Master Do file == | ==Components of a Master Do file == | ||
Since the master do file acts as a map to all the other do files in the project, it is important that the do file is organized and contains all the information necessary during the analysis. Some of the necessary components of a do file are as follows: | Since the master do file acts as a map to all the other do files in the project, it is important that the do file is organized and contains all the information necessary during the analysis. Some of the necessary components of a do file are as follows: | ||
=== Intro Header === | === Intro Header === | ||
The intro header should contain some descriptive information about the do file such that somebody who doesn't know the do file can read it and understand what the do file does and what it produces. | The intro header should contain some descriptive information about the do file such that somebody who doesn't know the do file can read it and understand what the do file does and what it produces. | ||
Some examples of information to put on the header are the purpose of the do file, the outline of the do file, the data files required to run the do file correctly, the data files created by the do file, the name variable that uniquely identifies the unit of observation in the datasets, etc. | Some examples of information to put on the header are the purpose of the do file, the outline of the do file, the data files required to run the do file correctly, the data files created by the do file, the name variable that uniquely identifies the unit of observation in the datasets, etc. | ||
=== Settings to Declare in the Master do-file=== | === Settings to Declare in the Master do-file=== | ||
After the intro header, settings that are used throughout the project should also be declared in the master do-file. Some of the settings are as follows: | After the intro header, settings that are used throughout the project should also be declared in the master do-file. Some of the settings are as follows: | ||
====Version Settings==== | ====Version Settings==== | ||
The version settings for Stata needs to be declared in the master do-file. Since, things like Stata's randomization algorithm sometimes changes across versions, it is important to declare Stata's version number to make sure that the analysis done using Stata is reproducible. | |||
::: Example: ''version 12.0'' | |||
====Basic and Advanced Memory Limits==== | ====Basic and Advanced Memory Limits==== | ||
Memory limits on Stata affect various things like the maximum number of variables a dataset can have (<code> maxvar</code>), number of variables than be used during Stata's estimation commands <code>matsize</code>, the amount and time Stata uses the system memory<code> niceness / min_memory / max_memory </code>, etc. Declaring the memory limits on the master do-files makes sure that the analysis runs smoothly with maximum efficiency. | |||
::: Example: ''set maxvar 20000'' | |||
====Default Options==== | ====Default Options==== | ||
Default options like setting more off/on, pause on/off, and abbreviation should also be set in the master do file. Declaring options in the main file ensures that when the other do-files are run through the master do file, the settings do not have to be declared again. | Default options like setting more off/on, pause on/off, and abbreviation should also be set in the master do file. Declaring options in the main file ensures that when the other do-files are run through the master do file, the settings do not have to be declared again. | ||
::: Example: ''set varabbrev off'' | |||
==== Standardization of Units and Assumptions ==== | ==== Standardization of Units and Assumptions ==== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 34: | ||
==== Installing any user written commands ==== | ==== Installing any user written commands ==== | ||
User written commands that need to be installed for the do-file should also be declared in the master do-file. Since, every computer that runs the code will not have the commands installed, it is necessary to install those commands. For example to install the command <code> outreg2 </code> used for exporting regression results in LaTeX and text formats, you should declare <code>ssc install outreg2, replace </code>. The <tt>replace</tt> makes sure that the latest version of the command with updated functionalities is installed if any previous versions have already been installed on the computer. | User written commands that need to be installed for the do-file should also be declared in the master do-file. Since, every computer that runs the code will not have the commands installed, it is necessary to install those commands. For example to install the command <code> outreg2 </code> used for exporting regression results in LaTeX and text formats, you should declare <code>ssc install outreg2, replace </code>. The <tt>replace</tt> makes sure that the latest version of the command with updated functionalities is installed if any previous versions have already been installed on the computer. | ||
==== Sub Master do-file(s) ==== | ==== Sub Master do-file(s) ==== | ||
Sub Master do-files are similar to a Master do-file except they perform a singular function, whereas the Master do-file runs all the necessary do-files from the raw data stage to the analysis and output stage. A sub Master-do file could be a do-file that runs all the do-files and commands used to generate all the graphs produced for a project. Instead of including each do-file that was used to produce the graphs needed for a project in the Master do-file, one could create a sub Master-do file for graphs outputs that will be called by the Master do-file. Following this technique one could have a sub Master do-file for graphs outputs, regressions, and data cleaning; all of which will be called upon by the Master do-file. | Sub Master do-files are similar to a Master do-file except they perform a singular function, whereas the Master do-file runs all the necessary do-files from the raw data stage to the analysis and output stage. A sub Master-do file could be a do-file that runs all the do-files and commands used to generate all the graphs produced for a project. Instead of including each do-file that was used to produce the graphs needed for a project in the Master do-file, one could create a sub Master-do file for graphs outputs that will be called by the Master do-file. Following this technique one could have a sub Master do-file for graphs outputs, regressions, and data cleaning; all of which will be called upon by the Master do-file. | ||
Revision as of 21:28, 10 February 2017
The master do-file is the main do file that is used to call upon all the other do files. By running this file, all files needed from importing raw data to cleaning, constructing, analysing and outputting results should be run. This file therefore also functions as a map to the data folder.
Read First
- The person creating the master do file should be able to run the do files from all stages(cleaning, construct, analysis, exporting tables, etc) from the master do-file and the someone else running the master do file should be able to run all of those just by changing the paths to their Dropbox/Box folders.
Components of a Master Do file
Since the master do file acts as a map to all the other do files in the project, it is important that the do file is organized and contains all the information necessary during the analysis. Some of the necessary components of a do file are as follows:
Intro Header
The intro header should contain some descriptive information about the do file such that somebody who doesn't know the do file can read it and understand what the do file does and what it produces. Some examples of information to put on the header are the purpose of the do file, the outline of the do file, the data files required to run the do file correctly, the data files created by the do file, the name variable that uniquely identifies the unit of observation in the datasets, etc.
Settings to Declare in the Master do-file
After the intro header, settings that are used throughout the project should also be declared in the master do-file. Some of the settings are as follows:
Version Settings
The version settings for Stata needs to be declared in the master do-file. Since, things like Stata's randomization algorithm sometimes changes across versions, it is important to declare Stata's version number to make sure that the analysis done using Stata is reproducible.
- Example: version 12.0
Basic and Advanced Memory Limits
Memory limits on Stata affect various things like the maximum number of variables a dataset can have ( maxvar), number of variables than be used during Stata's estimation commands matsize, the amount and time Stata uses the system memory niceness / min_memory / max_memory , etc. Declaring the memory limits on the master do-files makes sure that the analysis runs smoothly with maximum efficiency.
- Example: set maxvar 20000
Default Options
Default options like setting more off/on, pause on/off, and abbreviation should also be set in the master do file. Declaring options in the main file ensures that when the other do-files are run through the master do file, the settings do not have to be declared again.
- Example: set varabbrev off
Standardization of Units and Assumptions
Conversion rates for standardization of units and assumptions that need to be defined should be defined as globals in the master do-files. Varlist commonly used across the projects are also defined using globals/locals in the master do file. Since, globals defined in one do file also work on other do files throughout a Stata session, it is important to declare all the global variables necessary during the project on the master do-file.
Installing any user written commands
User written commands that need to be installed for the do-file should also be declared in the master do-file. Since, every computer that runs the code will not have the commands installed, it is necessary to install those commands. For example to install the command outreg2 used for exporting regression results in LaTeX and text formats, you should declare ssc install outreg2, replace . The replace makes sure that the latest version of the command with updated functionalities is installed if any previous versions have already been installed on the computer.
Sub Master do-file(s)
Sub Master do-files are similar to a Master do-file except they perform a singular function, whereas the Master do-file runs all the necessary do-files from the raw data stage to the analysis and output stage. A sub Master-do file could be a do-file that runs all the do-files and commands used to generate all the graphs produced for a project. Instead of including each do-file that was used to produce the graphs needed for a project in the Master do-file, one could create a sub Master-do file for graphs outputs that will be called by the Master do-file. Following this technique one could have a sub Master do-file for graphs outputs, regressions, and data cleaning; all of which will be called upon by the Master do-file.
Implementation
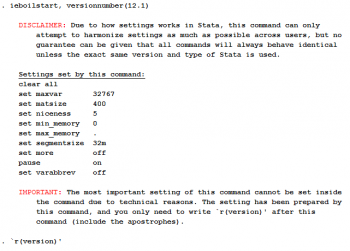
DIME's Stata command ieboilstart from the ietoolkit package declares all the necessary basic settings to standardize the code across multiple people working on the same project. This can be done adding the following 2 lines of code to every do-files.
ssc install ietoolkit, replace
ieboilstart, versionnumber(version_number) options
`r(version)'
Declaring these commands at the top of do file used by every member of the project ensures that the version settings are the same across all runs for the project. However, the globals and any extra commands installed should be declared as well.
Back to Parent
This article is part of the topic Data Management